What is Fatigue and Weakness?
Fatigue and weakness are commonly experienced symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Fatigue refers to a persistent feeling of tiredness or exhaustion that is not necessarily relieved by rest. It can be both physical and mental, often making it difficult to perform even simple tasks. Weakness, on the other hand, specifically refers to a lack of physical strength and a reduced capacity to exert force, which can make activities such as climbing stairs or lifting objects challenging.
While fatigue and weakness can stem from various causes, including lifestyle factors, chronic illnesses, and psychological conditions, they are also prevalent symptoms in numerous heart conditions. Understanding the relationship between heart health and these symptoms is crucial for identifying potential underlying cardiovascular issues and seeking appropriate treatment.
How Heart Conditions Affect Energy Levels
Heart conditions can significantly impact energy levels due to the crucial role the heart plays in delivering oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. When the heart is not functioning optimally, it can lead to reduced blood flow, which in turn affects the oxygen supply to muscles and organs. This reduction in oxygen can cause the body to work harder to perform routine activities, leading to increased feelings of fatigue and weakness.
Additionally, some heart conditions can cause fluid buildup in the lungs or other parts of the body, further impairing physical performance and leading to shortness of breath, which exacerbates fatigue. Understanding how specific heart conditions disrupt the body’s energy balance can help in recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely medical intervention.
Common Heart Conditions Leading to Fatigue
1. Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is one of the most common heart conditions that can cause fatigue and weakness. CAD occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This limits the amount of oxygen-rich blood reaching the heart, which can lead to chest pain, shortness of breath, and persistent fatigue. Patients with CAD often feel unusually tired, even after minimal exertion, as their heart struggles to pump blood effectively.
2. Heart Failure
Heart failure, also known as congestive heart failure, occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently. This condition results in reduced blood flow to the body’s organs and tissues, leading to symptoms such as extreme fatigue, weakness, and fluid retention. Individuals with heart failure often experience difficulty performing everyday activities, as their energy levels are significantly compromised. The chronic fatigue associated with heart failure can also contribute to a reduced quality of life and increased risk of complications.
3. Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats that can disrupt the normal rhythm and efficiency of the heart. These irregularities can range from harmless to life-threatening and can cause the heart to beat too quickly, too slowly, or irregularly. When the heart’s rhythm is abnormal, its ability to pump blood effectively is compromised, which can lead to feelings of dizziness, weakness, and severe fatigue. Some arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, are particularly known for causing chronic fatigue.
4. Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy refers to diseases of the heart muscle that make it harder for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body. This can be due to thickened, weakened, or rigid heart muscle, and it often leads to heart failure. The reduced cardiac output associated with cardiomyopathy means less oxygen and nutrients are delivered to the body’s tissues, which can cause persistent fatigue, weakness, and decreased exercise tolerance.
5. Valvular Heart Disease
Valvular heart disease involves damage or defects in one or more of the heart’s valves, which control blood flow through the heart. When these valves do not open or close properly, it can lead to disrupted blood flow and increased strain on the heart. This inefficiency can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, lightheadedness, and fatigue. Depending on the severity of the valvular issue, patients may experience varying degrees of fatigue that significantly impact their daily activities.
Symptoms of Heart-Related Fatigue
Fatigue caused by heart conditions can present with a variety of symptoms that may differ from ordinary tiredness. Common symptoms include a persistent sense of exhaustion that does not improve with rest, difficulty performing basic physical activities such as walking or climbing stairs, and a general lack of energy that impacts daily functioning. Patients may also experience additional symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness, chest pain, and swelling in the legs or ankles, all of which can further exacerbate feelings of fatigue and weakness.
It is important to note that heart-related fatigue often occurs without a clear cause and may worsen over time. If you experience persistent fatigue along with any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing Heart Conditions That Cause Fatigue
Diagnosing heart conditions that cause fatigue involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a review of medical history, a physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. Common diagnostic tests include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart and can help detect irregularities in heart rhythm, structure, and function that may be contributing to fatigue.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test uses sound waves to create images of the heart, allowing doctors to assess heart size, shape, and motion, as well as the function of the heart valves.
- Stress Test: A stress test evaluates how the heart performs under physical exertion, which can reveal issues with blood flow or heart function that are not apparent at rest.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify markers of heart disease, such as elevated cholesterol levels, markers of inflammation, or evidence of a previous heart attack.
- Coronary Angiography: This imaging test uses X-rays to view the heart’s blood vessels and can detect blockages or narrowing that may be causing reduced blood flow and fatigue.
Early diagnosis of heart conditions is key to managing symptoms and improving quality of life. If fatigue is suspected to be heart-related, these tests can help pinpoint the specific condition and guide appropriate treatment options.
Treatment Options for Heart Conditions and Fatigue
Treating heart conditions that cause fatigue involves addressing the underlying cardiovascular issues through a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, surgical interventions. The specific treatment approach will depend on the type and severity of the heart condition. Common treatment options include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can significantly improve energy levels and overall heart function. This includes eating a balanced diet low in saturated fats, regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stress. Weight management and limiting alcohol intake are also crucial in reducing symptoms of fatigue.
- Medications: Various medications can help manage heart conditions and alleviate symptoms. For example, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics can help improve heart function, regulate blood pressure, and reduce fluid buildup, thereby lessening fatigue. Anti-arrhythmic medications may be prescribed to control irregular heart rhythms.
- Medical Procedures: In some cases, medical procedures may be necessary to treat heart conditions. For example, angioplasty and stent placement can open blocked arteries, improving blood flow and reducing fatigue. Valve repair or replacement surgeries address valvular heart disease, while implantable devices such as pacemakers can help manage arrhythmias.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Cardiac rehabilitation programs provide a structured environment for patients to improve their cardiovascular health through monitored exercise, education, and support. These programs can help patients regain strength and reduce fatigue through personalized plans.
Effective management of heart conditions often leads to a reduction in fatigue and an improvement in overall quality of life. It is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a treatment plan tailored to their specific needs.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Energy Levels
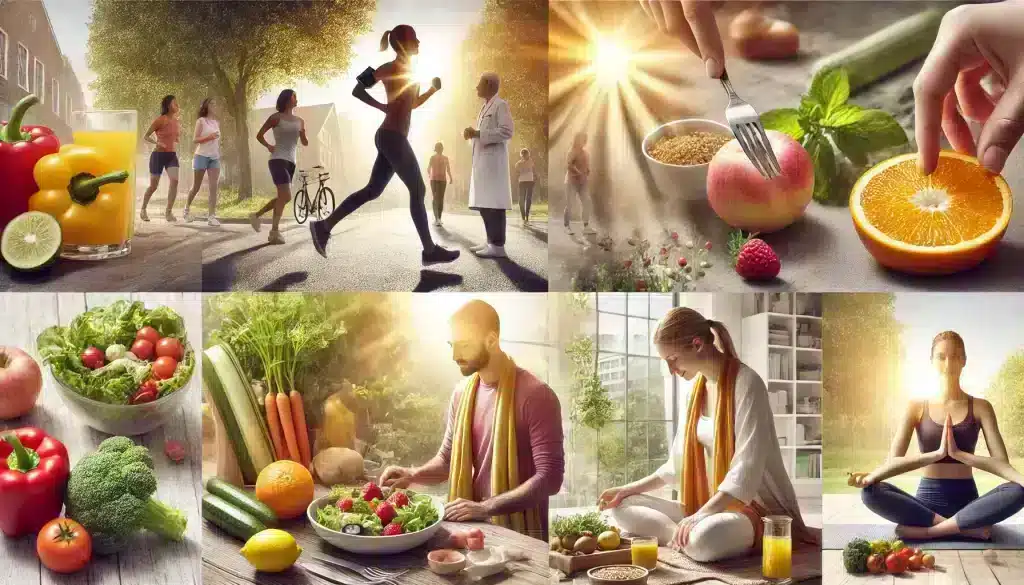

Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly help in managing fatigue and boosting energy levels, especially when dealing with heart conditions. These changes not only support heart health but also improve overall well-being. Key lifestyle modifications include:
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular, moderate exercise such as walking, swimming, or cycling can strengthen the heart and improve circulation, leading to increased energy levels. It is important to start slowly and gradually increase activity levels as tolerated.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide the necessary nutrients to support heart health and energy production. Reducing salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats can also help manage symptoms of heart conditions.
- Proper Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for maintaining energy levels and overall health. Establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a restful sleep environment can improve the quality of rest and reduce fatigue.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate heart conditions and lead to fatigue. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help manage stress levels and improve energy.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining energy levels. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, so it’s important to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially during physical activity.
Implementing these lifestyle changes can make a significant difference in managing fatigue and enhancing quality of life for those with heart conditions. Consistent efforts towards a healthier lifestyle can lead to gradual but noticeable improvements in energy and overall health.
When to See a Doctor
Fatigue and weakness, while common symptoms, can sometimes be indicators of underlying heart conditions that require medical attention. It is important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience persistent fatigue that does not improve with rest, or if fatigue is accompanied by symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or swelling in the legs and ankles. These symptoms may suggest a more serious cardiovascular issue that needs prompt evaluation and treatment.
Early diagnosis and management of heart conditions can prevent complications and improve quality of life. Do not hesitate to seek medical advice if you have concerns about your energy levels or if your symptoms worsen over time. A healthcare provider can conduct a thorough assessment, including necessary diagnostic tests, to determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Regular check-ups and monitoring are also important for individuals with known heart conditions to manage their symptoms effectively and to adjust treatments as needed. Proactive healthcare can make a significant difference in managing fatigue and maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle.
FAQs About Heart Conditions and Fatigue
What heart conditions are most commonly associated with fatigue?
Common heart conditions associated with fatigue include coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy, and valvular heart disease. These conditions affect the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently, leading to reduced oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues and causing fatigue.
Can lifestyle changes alone improve fatigue caused by heart conditions?
While lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and adequate sleep can significantly improve energy levels, they are often part of a broader treatment plan that may include medications or medical procedures. It’s important to follow a comprehensive approach tailored to the specific heart condition.
How is fatigue from heart conditions different from normal tiredness?
Fatigue related to heart conditions is often persistent and does not improve with rest. It can be accompanied by other symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness, and swelling. Unlike normal tiredness, heart-related fatigue is usually linked to reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery caused by underlying cardiovascular issues.
What tests are used to diagnose heart conditions that cause fatigue?
Common diagnostic tests include an electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, stress tests, blood tests, and coronary angiography. These tests help evaluate the heart’s structure, function, and blood flow to determine the cause of fatigue.
When should I seek medical attention for fatigue?
You should seek medical attention if you experience persistent fatigue that does not improve with rest, or if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or swelling. Early consultation with a healthcare provider can lead to timely diagnosis and effective management of any underlying heart condition.