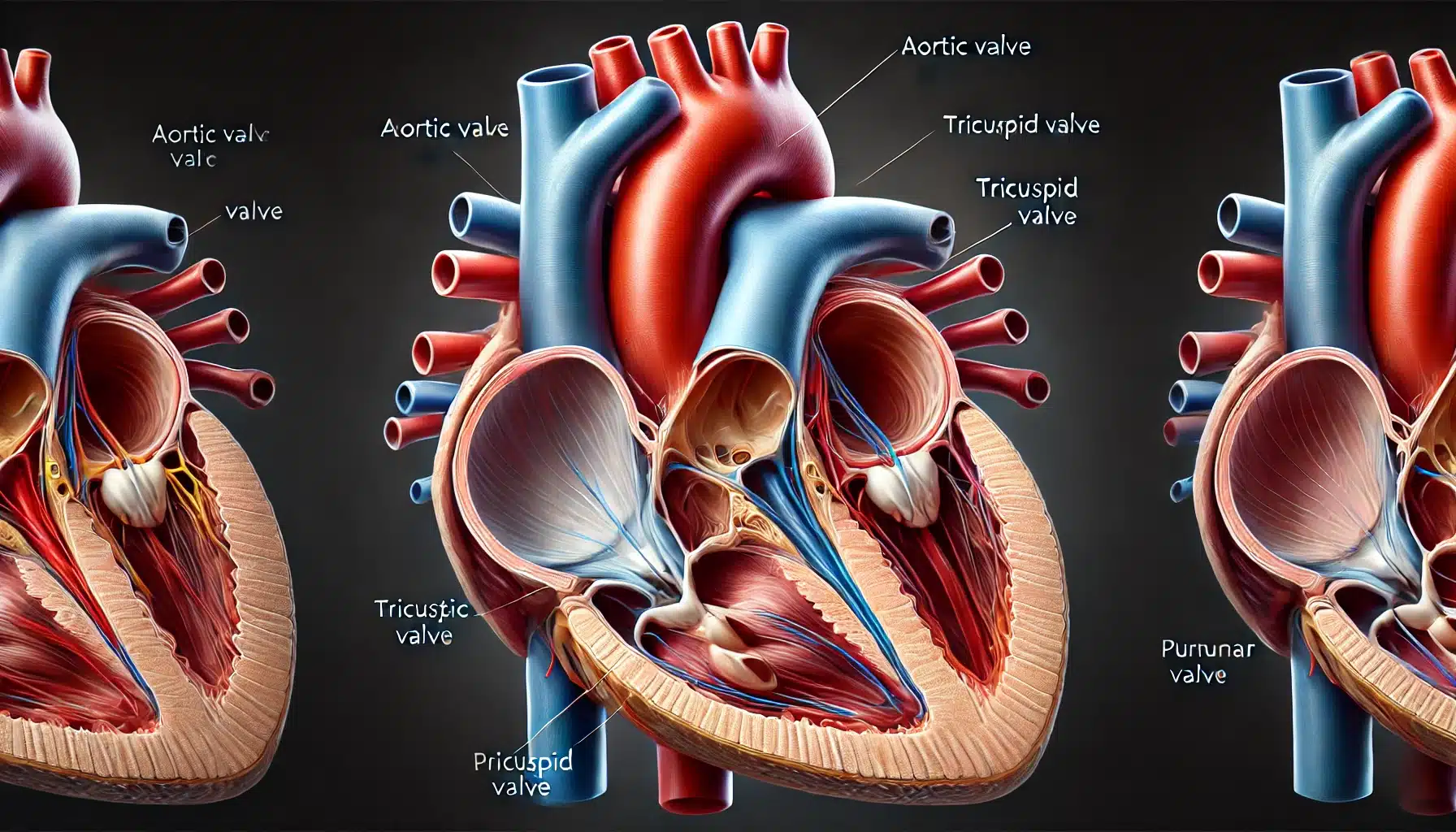
Introduction to Heart Valve Replacement
Latest Advances in Heart Valve Replacement Techniques. Heart valve replacement is a critical procedure for patients suffering from severe valve dysfunctions, such as stenosis or regurgitation. The heart valves play an essential role in regulating blood flow through the heart’s chambers, ensuring that blood moves in the correct direction. When a valve is damaged or diseased, it can significantly impact heart function, leading to symptoms like breathlessness, chest pain, and even heart failure. As a result, replacing a malfunctioning valve is often necessary to restore normal heart function and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Over the past few decades, advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques have greatly improved the success rates of heart valve replacement procedures. These advances have introduced a variety of options that cater to the specific needs and conditions of each patient, ranging from traditional surgical methods to less invasive approaches. Understanding the latest techniques and their benefits can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about heart valve replacement.
Types of Heart Valve Replacement Procedures
Heart valve replacement procedures can be broadly categorized into two main types: surgical valve replacement and transcatheter valve replacement. Each approach offers distinct advantages and is selected based on the patient’s condition, age, and overall health.
Surgical Valve Replacement
Surgical valve replacement, often referred to as open-heart surgery, has been the traditional method for replacing damaged heart valves. This approach involves making a large incision in the chest to access the heart, stopping the heart temporarily, and replacing the faulty valve with a new one. There are two primary types of surgical valve replacements:
- Mechanical Valves: Made from durable materials such as titanium or carbon, mechanical valves are designed to last a lifetime. However, they require patients to take lifelong blood-thinning medication to prevent blood clots.
- Bioprosthetic Valves: These valves are made from animal tissue, such as pig or cow valves, or human donor valves. They do not require long-term anticoagulation therapy but may need to be replaced after 10-20 years due to wear.
Transcatheter Valve Replacement
Transcatheter valve replacement is a less invasive procedure compared to traditional surgery. It involves inserting a replacement valve through a catheter, usually from the groin, and guiding it to the heart. This method is particularly beneficial for patients who are high-risk candidates for surgery due to age or other health conditions. The most common type of this procedure is Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR).
- Benefits of TAVR: This approach eliminates the need for open-heart surgery, reduces recovery time, and lowers the risk of complications.
- Limitations of TAVR: TAVR is currently recommended primarily for aortic valve replacement and may not be suitable for all types of valve diseases.
Recent Innovations in Heart Valve Technology
 Recent years have seen remarkable innovations in heart valve technology, significantly enhancing the outcomes of replacement procedures. These advancements aim to improve the longevity of replacement valves, reduce the need for repeated surgeries, and provide options for patients who may not be suitable candidates for traditional surgery.
Recent years have seen remarkable innovations in heart valve technology, significantly enhancing the outcomes of replacement procedures. These advancements aim to improve the longevity of replacement valves, reduce the need for repeated surgeries, and provide options for patients who may not be suitable candidates for traditional surgery.
Bioprosthetic Valves
Bioprosthetic valves have evolved with the introduction of advanced tissue engineering techniques. These valves, made from biological tissues, are increasingly treated with special processes to improve their durability and reduce the likelihood of calcification, a common issue that can lead to valve failure.
- Advanced Tissue Processing: Techniques like decellularization, which removes cellular material from the valve, have been developed to minimize the immune response and enhance the valve’s durability.
- Longer Lifespan: Modern bioprosthetic valves are designed to last longer than earlier versions, potentially reducing the need for repeat surgeries.
Mechanical Valves
Mechanical valves have also seen significant improvements, particularly in their design and the materials used. These innovations aim to reduce complications and enhance the functionality of the valves over the patient’s lifetime.
- Improved Designs: Newer mechanical valves feature designs that mimic natural valve movement more closely, leading to better hemodynamics and reduced wear.
- Advanced Materials: The use of advanced materials such as carbon-coated components has reduced the risk of clot formation, potentially lowering the dosage of blood thinners required.
Minimally Invasive Valve Replacement Techniques
The shift towards minimally invasive techniques has been one of the most significant advancements in heart valve replacement. These methods offer several benefits, including reduced recovery time and fewer complications.
- Smaller Incisions: Minimally invasive surgeries involve smaller incisions, leading to less pain and faster recovery times.
- Robotic Assistance: Some procedures now use robotic systems, allowing for greater precision and reduced trauma to surrounding tissues.
- Hybrid Procedures: Combining surgical and transcatheter approaches, hybrid procedures offer tailored solutions for patients with complex valve diseases.
Advantages and Challenges of New Techniques
The advancements in heart valve replacement techniques offer numerous benefits, but they also come with their own set of challenges. Understanding these pros and cons can help in making the right treatment decisions for patients.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive heart valve replacement techniques provide several advantages over traditional open-heart surgery, making them a preferred option for many patients and surgeons alike:
- Reduced Recovery Time: Patients undergoing minimally invasive procedures typically experience faster recovery times and shorter hospital stays compared to those who have traditional surgery.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions reduce the risk of infection and minimize scarring, leading to better cosmetic outcomes and lower healthcare costs.
- Less Pain and Discomfort: With less tissue disruption, patients report less pain and discomfort post-operation, enhancing overall patient satisfaction.
Risks and Complications
Despite the many benefits, heart valve replacement procedures are not without risks. Complications can vary depending on the type of procedure and the patient’s overall health condition:
- Valve Dysfunction: Both mechanical and bioprosthetic valves can malfunction over time, requiring additional interventions or replacement.
- Blood Clots: Mechanical valves pose a higher risk of blood clots, necessitating lifelong anticoagulation therapy, which can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Paravalvular Leak: In transcatheter procedures, there is a potential for leaks around the valve, which may require further treatment.
- Patient-Specific Factors: Age, comorbidities, and the specific type of valve disease can all influence the likelihood of complications.
Patient Outcomes and Future Directions
Advancements in heart valve replacement techniques have significantly improved patient outcomes, leading to better quality of life and increased survival rates. However, ongoing research continues to explore new ways to enhance these results further.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
Effective post-operative care is crucial for the success of heart valve replacement procedures. Key components of recovery include:
- Regular Monitoring: Patients require regular follow-ups with their cardiologist to monitor valve function and detect any signs of complications early.
- Medication Management: Managing medications, particularly blood thinners for mechanical valve recipients, is critical to preventing clot-related complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Patients are often advised to make lifestyle changes, such as improving their diet, engaging in moderate exercise, and avoiding smoking, to support overall heart health.
Future Trends in Heart Valve Replacement
The future of heart valve replacement is focused on developing even less invasive techniques, improving valve durability, and expanding the indications for various procedures:
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in imaging and diagnostics are paving the way for personalized valve replacement strategies tailored to individual patient anatomy and needs.
- Next-Generation Valves: Research is underway to develop valves that can grow with pediatric patients or self-repair over time, reducing the need for future replacements.
- Biodegradable Valves: Innovations in biodegradable materials could lead to valves that naturally degrade after they are no longer needed, eliminating the risk of long-term complications.
Conclusion
Heart valve replacement has come a long way, with significant advancements in both surgical and transcatheter techniques. These innovations have not only improved the success rates of the procedures but have also expanded the options available to patients, allowing for more personalized and less invasive treatments. As technology continues to evolve, the future of heart valve replacement looks promising, with ongoing research aimed at developing even more effective and durable solutions.
For patients and healthcare providers, staying informed about the latest advances in heart valve replacement is crucial for making the best possible decisions regarding treatment options. Whether through traditional surgery or the latest minimally invasive techniques, the goal remains the same: to restore heart function and enhance the quality of life for patients suffering from valve diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the risks associated with heart valve replacement?
While heart valve replacement procedures are generally safe, there are risks such as blood clots, valve dysfunction, and paravalvular leaks. The specific risks depend on the type of procedure and the patient’s health condition.
How long do replacement heart valves last?
Bioprosthetic valves typically last 10-20 years, while mechanical valves are designed to last a lifetime. However, mechanical valves require lifelong anticoagulation therapy to prevent blood clots.
What is the recovery time for heart valve replacement surgery?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of procedure. Traditional open-heart surgery may require several weeks to a few months for full recovery, while minimally invasive procedures often result in shorter recovery times.
Are there alternatives to heart valve replacement?
In some cases, valve repair may be an option, particularly for mitral valve prolapse. However, when the valve is too damaged, replacement is the preferred option.
What are the latest innovations in heart valve replacement?
Recent innovations include minimally invasive techniques like TAVR, advanced bioprosthetic valves with longer lifespans, and research into biodegradable and self-repairing valves.