1. Introduction to Cardiac Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation is a medically supervised program designed to improve the cardiovascular health of patients diagnosed with coronary artery disease (CAD). The rehabilitation process plays a crucial role in helping patients recover from heart-related conditions and surgeries while significantly reducing the risk of future cardiac events. Through a combination of exercise, education, and lifestyle changes, cardiac rehabilitation offers a comprehensive approach to improving heart health and overall well-being.

Coronary artery disease is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality globally. For individuals diagnosed with CAD, undergoing cardiac rehabilitation can not only speed up recovery but also improve long-term health outcomes. This program is particularly beneficial for patients who have experienced heart attacks, undergone coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), or had stents implanted. The focus of cardiac rehabilitation is not only to strengthen the heart but also to address other risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity.
- Medically supervised exercise programs
- Patient education on heart-healthy living
- Counseling to reduce stress and improve mental health
2. Key Components of Cardiac Rehabilitation
2.1 Exercise Training
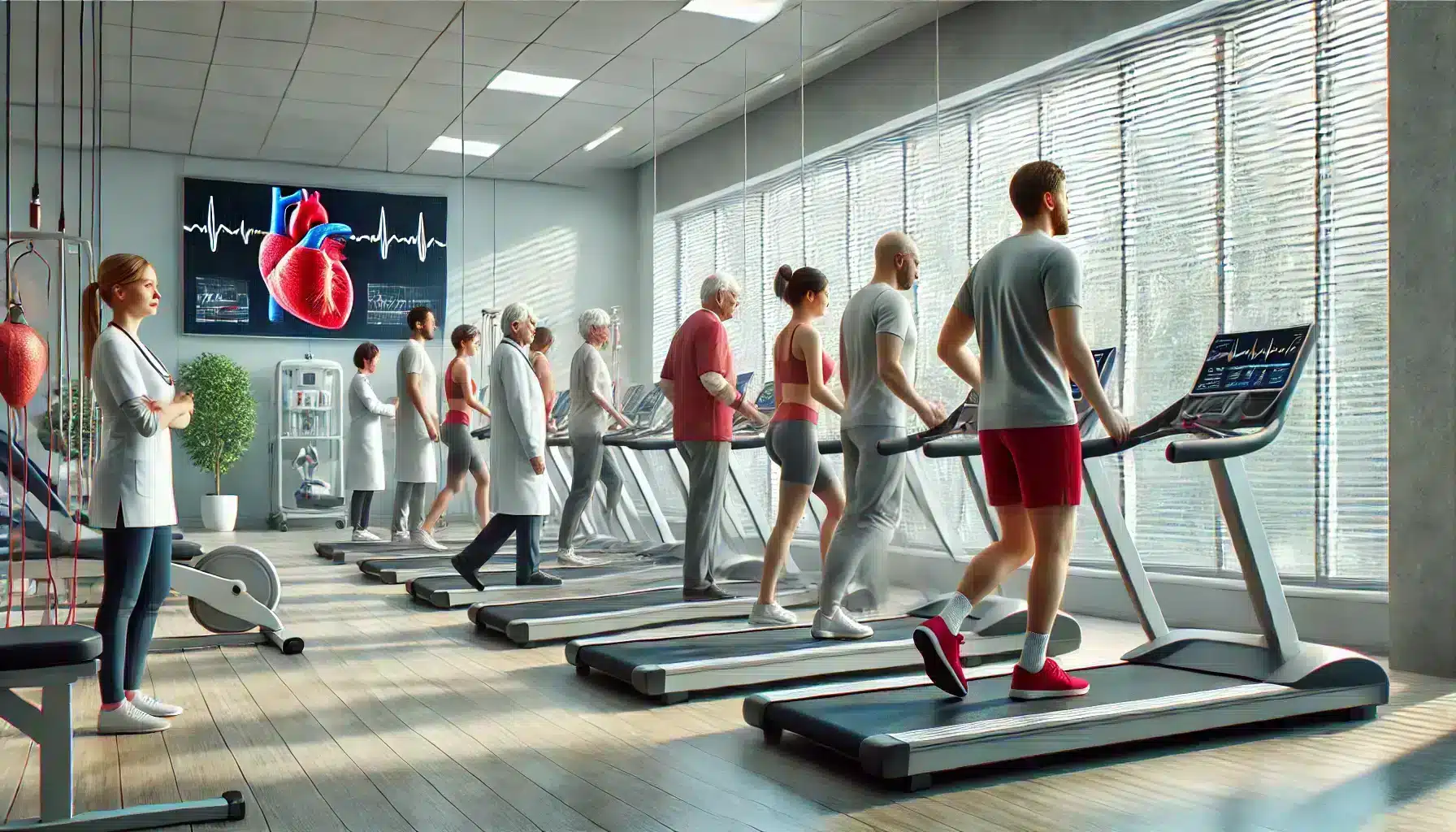
Exercise training is one of the cornerstone components of cardiac rehabilitation. Under the supervision of healthcare professionals, patients engage in structured physical activity tailored to their individual health status and needs. The goal of exercise training is to improve cardiovascular fitness, strengthen the heart muscle, and increase the overall endurance of the patient.
Patients typically start with low-intensity exercises, such as walking or stationary cycling, and gradually increase the intensity as their fitness improves. Each exercise session is carefully monitored to ensure that the patient’s heart rate and blood pressure remain within safe ranges. Over time, consistent exercise helps to reduce the workload on the heart, improve circulation, and lower the risk of future cardiac events.
- Improved heart function and cardiovascular fitness
- Reduced risk of hospital readmissions
- Increased muscle strength and endurance
2.2 Education and Counseling
Education is another critical element of cardiac rehabilitation. Patients are taught about heart-healthy habits and lifestyle changes that can significantly improve their condition and prevent the progression of coronary artery disease. This includes dietary advice, smoking cessation support, and strategies for managing stress. Educational sessions are often led by dietitians, nurses, and other healthcare providers who specialize in cardiovascular health.
In addition to education, counseling services are offered to help patients cope with the emotional and psychological challenges that come with living with CAD. Many patients experience anxiety, depression, or fear of another cardiac event, and these feelings can hinder their recovery. Counseling helps patients build emotional resilience, fostering a positive outlook and encouraging adherence to rehabilitation protocols.
- Heart-healthy dietary guidance
- Support for mental health and well-being
- Strategies for managing stress and reducing anxiety
2.3 Risk Factor Modification
A major focus of cardiac rehabilitation is modifying risk factors that contribute to the development and progression of CAD. Patients work with their healthcare teams to manage conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity, which are all significant contributors to heart disease. Through medication management, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring, patients can significantly lower their risk of further heart complications.
Risk factor modification is a continuous process that requires long-term commitment from patients. It involves adopting a heart-healthy diet, staying physically active, taking prescribed medications, and avoiding unhealthy behaviors such as smoking. The overall goal is to empower patients to take control of their health and reduce the likelihood of another cardiac event.
- Lowered blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Better diabetes management
- Reduced body weight and improved physical health
3. Evidence-Based Benefits for CAD Patients

3.1 Reduced Mortality and Morbidity
One of the most significant benefits of cardiac rehabilitation for CAD patients is the reduction in both mortality and morbidity. Numerous studies have shown that patients who complete a cardiac rehabilitation program are less likely to experience a second heart attack, undergo coronary interventions, or die from heart disease. These programs provide structured support for lifestyle modifications, which, combined with medical treatment, lead to improved heart health and longevity.
Research has consistently demonstrated that participation in cardiac rehabilitation can decrease the risk of death from heart-related causes by up to 25%. This makes it a highly effective intervention for CAD patients, especially when compared to standard medical treatment alone. The combination of exercise, education, and support provided through rehabilitation helps strengthen the cardiovascular system, reduces stress on the heart, and enhances overall quality of life.
- 25% reduction in heart-related mortality
- Lower risk of future cardiac events
- Improved heart function and endurance
3.2 Improved Quality of Life
Cardiac rehabilitation not only improves physical health but also enhances the overall quality of life for CAD patients. By participating in regular physical activity, learning how to manage their condition, and receiving emotional support, patients report feeling more in control of their health. They experience fewer symptoms of CAD, such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath, which significantly improves their daily functioning.
Furthermore, the psychological support provided during cardiac rehabilitation plays a vital role in improving mental health. Patients often struggle with anxiety, depression, and fear following a heart attack or other cardiac event. Rehabilitation programs offer counseling and stress management techniques, which help alleviate these emotional burdens, leading to a more positive outlook and greater life satisfaction.
- Reduced symptoms of CAD (e.g., chest pain, fatigue)
- Enhanced mental health and emotional well-being
- Greater independence in daily activities
3.3 Decreased Hospital Readmissions
Hospital readmissions are a common issue for patients with CAD, especially in the months following a heart attack or surgery. Cardiac rehabilitation has been shown to reduce the rate of hospital readmissions by helping patients manage their symptoms more effectively and adhere to prescribed treatments. By addressing risk factors and providing ongoing support, rehabilitation minimizes the likelihood of complications that would otherwise require further hospitalization.
In addition, patients who engage in cardiac rehabilitation are more likely to follow their prescribed medication regimens and attend follow-up appointments with their healthcare providers. This increased compliance with medical care helps prevent the worsening of their condition and reduces the need for emergency interventions.
- Fewer hospitalizations and emergency visits
- Improved medication adherence
- Better management of symptoms
3.4 Enhanced Physical and Mental Health
The benefits of cardiac rehabilitation extend beyond the heart; it also improves overall physical and mental health. Regular exercise strengthens muscles, enhances flexibility, and boosts endurance, allowing patients to perform daily tasks with greater ease. This physical transformation is particularly important for CAD patients who may have been sedentary or restricted in their activities due to heart disease.
Mental health also sees significant improvements during cardiac rehabilitation. The support patients receive from healthcare providers, as well as their peers in the program, helps build a sense of community and accountability. This camaraderie, along with the psychological counseling offered, helps reduce feelings of isolation, anxiety, and depression, promoting a more positive mental state.
- Increased physical strength and stamina
- Improved flexibility and mobility
- Better emotional well-being and social support
4. Challenges and Barriers to Cardiac Rehabilitation

4.1 Access to Programs
Despite the proven benefits of cardiac rehabilitation, many patients face challenges in accessing these programs. Geographic location is one of the primary barriers, as some regions lack sufficient rehabilitation facilities, particularly in rural or underserved areas. In such cases, patients may have to travel long distances to attend sessions, which can be a significant obstacle, especially for those with limited mobility or transportation options.
Financial constraints also pose a challenge for many CAD patients. Although insurance coverage for cardiac rehabilitation has improved in recent years, some patients may still face out-of-pocket costs that prevent them from enrolling in the program. Additionally, time constraints, especially for working individuals or caregivers, make it difficult for some to commit to the structured schedule of rehabilitation sessions.
- Limited availability in rural or underserved areas
- Financial barriers, including out-of-pocket costs
- Time constraints and competing responsibilities
4.2 Patient Adherence and Motivation
Patient adherence to cardiac rehabilitation programs is another major challenge. While the benefits are well-documented, some patients struggle with maintaining motivation throughout the course of the program. This can be due to a variety of factors, including physical limitations, emotional distress, or a lack of understanding about the long-term benefits of rehabilitation. Ensuring that patients stay engaged and committed to the program is critical to achieving the desired health outcomes.
Healthcare providers play a key role in supporting patient adherence by offering encouragement, setting achievable goals, and providing continuous feedback on progress. However, some patients may require additional motivational strategies, such as peer support groups or digital health tools, to stay on track. Programs that integrate technology, such as mobile apps for tracking progress or virtual check-ins with healthcare professionals, have shown promise in improving adherence.
- Physical limitations that affect participation
- Lack of motivation or emotional distress
- Need for continuous support and engagement strategies
5. Future Directions and Research in Cardiac Rehabilitation
5.1 Emerging Technologies in Cardiac Rehabilitation
 The field of cardiac rehabilitation is evolving with the integration of new technologies designed to enhance patient outcomes and expand access to care. One of the most promising developments is the rise of tele-rehabilitation, which allows patients to participate in cardiac rehabilitation programs remotely. This is especially beneficial for patients who live in rural areas or those with limited mobility. Tele-rehabilitation typically involves virtual consultations, remote monitoring of vital signs, and online exercise programs guided by healthcare professionals.
The field of cardiac rehabilitation is evolving with the integration of new technologies designed to enhance patient outcomes and expand access to care. One of the most promising developments is the rise of tele-rehabilitation, which allows patients to participate in cardiac rehabilitation programs remotely. This is especially beneficial for patients who live in rural areas or those with limited mobility. Tele-rehabilitation typically involves virtual consultations, remote monitoring of vital signs, and online exercise programs guided by healthcare professionals.
Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and heart rate monitors, are also playing a growing role in cardiac rehabilitation. These devices enable continuous tracking of a patient’s activity levels, heart rate, and other key metrics, providing real-time feedback that can be used to adjust rehabilitation programs. Patients and healthcare providers can review this data to ensure that the patient is progressing safely and effectively.
- Tele-rehabilitation for remote access to care
- Wearable technology for real-time monitoring
- Mobile apps to track progress and enhance engagement
5.2 Personalized Rehabilitation Programs
Another exciting direction in cardiac rehabilitation is the move toward personalized rehabilitation programs. Advances in genetic research, personalized medicine, and data analytics are enabling healthcare providers to tailor rehabilitation programs to the unique needs of each patient. Instead of a one-size-fits-all approach, personalized rehabilitation takes into account factors such as a patient’s genetic predisposition to heart disease, medical history, lifestyle, and risk factors.
Personalized rehabilitation programs can offer more targeted interventions, such as specific dietary recommendations, exercise plans, and medication regimens. This level of customization ensures that patients receive the most effective care possible, increasing their chances of long-term success and reducing the risk of future cardiac events.
- Tailored exercise and dietary plans
- Individualized risk factor management
- More effective, patient-specific care strategies
6. Conclusion
Cardiac rehabilitation is a highly effective intervention for patients with coronary artery disease, offering numerous benefits that improve both short-term and long-term health outcomes. By focusing on exercise, education, risk factor modification, and emotional support, cardiac rehabilitation helps patients regain control of their heart health and significantly reduces the risk of future cardiac events.
While challenges such as access to programs and patient adherence remain, ongoing advancements in technology and personalized medicine are expanding the reach and effectiveness of rehabilitation programs. As research continues to evolve, the future of cardiac rehabilitation looks promising, with the potential for even greater improvements in patient care and recovery outcomes.
For CAD patients, participating in a cardiac rehabilitation program is one of the most impactful steps they can take towards better heart health and overall quality of life. With continued support from healthcare providers and ongoing innovations in rehabilitation practices, patients can achieve long-lasting improvements in both physical and mental well-being.
FAQ
What is cardiac rehabilitation?
Cardiac rehabilitation is a medically supervised program that helps people with heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease, improve their cardiovascular health through structured exercise, education, and lifestyle modifications.
How does cardiac rehabilitation benefit CAD patients?
Cardiac rehabilitation offers numerous benefits for CAD patients, including reduced mortality, improved quality of life, decreased hospital readmissions, and enhanced physical and mental health. It helps patients regain control of their heart health and reduces the risk of future heart events.
What are the key components of a cardiac rehabilitation program?
The key components of cardiac rehabilitation include exercise training, education and counseling, and risk factor modification. These elements work together to strengthen the heart, promote a healthier lifestyle, and support long-term cardiovascular health.
Can cardiac rehabilitation be done at home?
Yes, with advancements in technology, tele-rehabilitation allows patients to participate in cardiac rehabilitation programs remotely. This is particularly beneficial for those who live in rural areas or have mobility issues. Wearable devices and mobile apps can also help monitor progress from home.
Who is eligible for cardiac rehabilitation?
Cardiac rehabilitation is typically recommended for individuals who have experienced heart attacks, undergone heart surgery, or have conditions such as coronary artery disease. It is important to consult a healthcare provider to determine eligibility for the program.