Common Causes of Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea, is a condition where you feel an intense tightening in your chest, air hunger, difficulty breathing, or a feeling of suffocation. This sensation can be unsettling and may range from mild to severe. Understanding the common causes of shortness of breath is crucial for managing it effectively at home.
Several factors can lead to shortness of breath. Some of the most common causes include respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia. Cardiovascular issues like heart failure, arrhythmias, or coronary artery disease can also contribute to this condition. Additionally, anxiety, obesity, and exposure to allergens or pollutants can trigger episodes of shortness of breath.
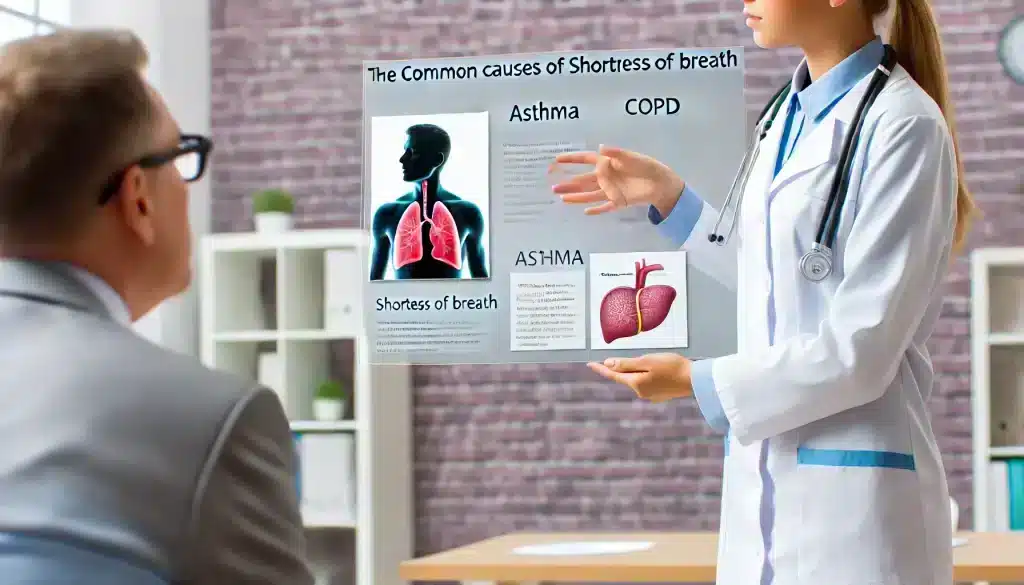

It’s important to note that while some causes are benign and manageable at home, others may require immediate medical attention. For instance, if shortness of breath is sudden, severe, or accompanied by chest pain, it could be a sign of a heart attack or pulmonary embolism, which are medical emergencies.
- Respiratory conditions: Asthma, COPD, pneumonia
- Cardiovascular issues: Heart failure, arrhythmias, coronary artery disease
- Other factors: Anxiety, obesity, allergens, pollutants
Home Management Strategies for Shortness of Breath
Managing shortness of breath at home involves a combination of immediate relief techniques and long-term strategies. These methods aim to reduce the severity and frequency of episodes, improve overall lung function, and enhance quality of life. Below are some effective strategies to help you manage shortness of breath in a home setting.
First, focusing on proper breathing techniques can make a significant difference. Breathing exercises, such as pursed-lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing, can help slow your breathing rate and increase your lung capacity. These exercises are particularly beneficial during an acute episode of breathlessness, allowing more air to flow in and out of your lungs.

Adjusting your environment is another critical step. Ensuring your living space is well-ventilated, free from allergens, and at a comfortable temperature can help reduce the strain on your respiratory system. Using air purifiers or humidifiers can also assist in maintaining optimal air quality and humidity levels, which are essential for comfortable breathing.
- Breathing exercises: Pursed-lip breathing, diaphragmatic breathing
- Environmental adjustments: Good ventilation, allergen control, optimal temperature
- Humidity control: Using humidifiers or dehumidifiers as needed
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Breathing
Incorporating lifestyle changes is a crucial component of managing shortness of breath. These changes not only help in reducing the frequency of breathlessness episodes but also contribute to overall health improvement. By focusing on aspects like diet, exercise, weight management, and stress reduction, you can enhance your respiratory function and quality of life.
Diet and Nutrition Tips: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports overall health, including respiratory function. Avoiding foods that can cause bloating or acid reflux, such as fatty or fried foods, can also help reduce pressure on your diaphragm and lungs, making breathing easier.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, can put additional pressure on your lungs and diaphragm, making it harder to breathe. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help manage weight and improve lung capacity. Even moderate exercise can have significant benefits for your breathing and overall cardiovascular health.
Stress Management Techniques: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate shortness of breath. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help calm the mind and body, reducing the likelihood of anxiety-induced breathlessness. Prioritizing activities that promote relaxation and mental well-being is essential for those dealing with chronic respiratory issues.
- Balanced diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Weight management: Regular physical activity to reduce abdominal pressure
- Stress reduction: Yoga, meditation, and relaxation techniques
Medications and Devices for Home Use
For those experiencing shortness of breath, there are several medications and devices that can be used at home to provide relief. Understanding how to properly use these options is key to managing symptoms effectively. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication or using any medical device.
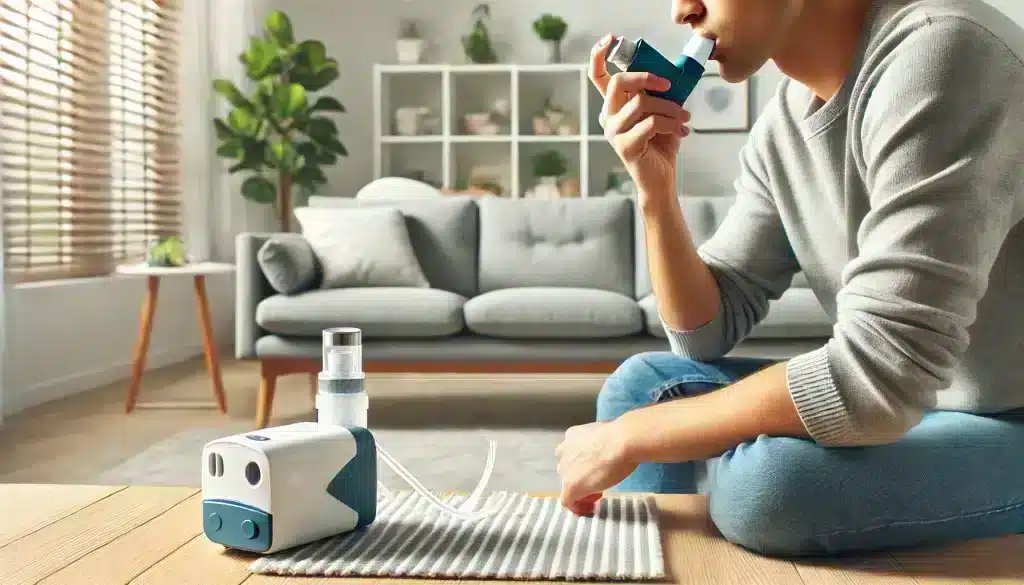

Over-the-Counter Medications: Some over-the-counter medications, such as antihistamines and decongestants, can help alleviate shortness of breath caused by allergies or nasal congestion. These medications reduce inflammation and clear nasal passages, making it easier to breathe. However, they should be used cautiously, especially in individuals with cardiovascular issues, as they can have side effects like increased heart rate.
Inhalers and Nebulizers: Inhalers and nebulizers are commonly prescribed for individuals with respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD. These devices deliver medication directly to the lungs, helping to open airways and reduce inflammation. Inhalers are portable and convenient for quick relief, while nebulizers are typically used for more severe symptoms, delivering medication in the form of a mist over a longer period.
Oxygen Therapy: When is it Necessary? In cases where shortness of breath is due to low oxygen levels in the blood, oxygen therapy may be necessary. This therapy involves breathing in supplemental oxygen through a mask or nasal cannula to increase the amount of oxygen in the blood. It’s often used for individuals with severe COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, or other chronic lung diseases. Oxygen therapy should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as improper use can lead to complications.
- Over-the-counter medications: Antihistamines, decongestants
- Inhalers and nebulizers: For asthma, COPD
- Oxygen therapy: Used under medical supervision for chronic lung diseases
Preventing Shortness of Breath Episodes
Prevention is a key aspect of managing shortness of breath, especially for individuals with chronic conditions that predispose them to respiratory difficulties. By identifying and avoiding triggers, maintaining regular exercise, and protecting your lungs from pollutants and allergens, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of breathlessness episodes.

Identifying Triggers: Understanding what triggers your shortness of breath is the first step in prevention. Common triggers include allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, as well as environmental factors such as smoke, strong odors, or cold air. Keeping a journal of your symptoms and possible triggers can help you identify patterns and avoid situations that exacerbate your breathing difficulties.
Regular Exercise and Its Benefits: Regular physical activity strengthens your cardiovascular and respiratory systems, making them more efficient at delivering oxygen throughout your body. Engaging in activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can improve lung capacity and reduce breathlessness over time. It’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity of your workouts, always listening to your body and avoiding overexertion.
Avoiding Pollutants and Allergens: Limiting exposure to pollutants and allergens is crucial for preventing shortness of breath. This includes avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke, using air purifiers to reduce indoor allergens, and wearing a mask when outdoor air quality is poor. If you have allergies, keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons and regularly cleaning your home can help minimize allergen exposure.
- Identify triggers: Keep a journal to track symptoms and triggers
- Exercise regularly: Focus on activities like walking, swimming, yoga
- Avoid pollutants: Use air purifiers, avoid smoke, and manage allergens
Understanding Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, or dyspnea, is a symptom that can result from a wide range of health issues, from mild conditions like anxiety or obesity to serious medical problems such as heart disease or lung disorders. It’s characterized by the feeling of being unable to get enough air, tightness in the chest, or labored breathing. Understanding the underlying causes and mechanisms of shortness of breath is essential for managing it effectively at home.
Shortness of breath can be categorized as acute or chronic. Acute shortness of breath comes on suddenly and may be due to conditions like asthma attacks, allergic reactions, or infections such as pneumonia. Chronic shortness of breath, on the other hand, develops over time and is often associated with long-term conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart failure, or severe obesity.
Various factors influence how shortness of breath is experienced and managed. The intensity and duration of symptoms can vary widely depending on the cause and individual health status. For instance, someone with mild asthma may experience shortness of breath during exercise or in cold weather, while a person with severe COPD might struggle with breathlessness even at rest. Understanding the specific factors contributing to your symptoms can help tailor an effective management plan.
- Acute causes: Asthma attacks, allergic reactions, infections
- Chronic causes: COPD, heart failure, obesity
- Symptom variability: Depends on underlying cause and individual health
When to Seek Medical Help
While managing shortness of breath at home can be effective for mild cases, there are times when medical intervention is necessary. Recognizing when to seek medical help is crucial, as some causes of shortness of breath can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s important to contact a healthcare provider immediately.
Sudden and Severe Shortness of Breath: If you suddenly feel breathless without a clear reason, especially if it’s severe and persistent, it could indicate a serious condition like a heart attack, pulmonary embolism, or pneumothorax (collapsed lung). These conditions require emergency medical care, as they can rapidly worsen without treatment.
Shortness of Breath Accompanied by Chest Pain: If your shortness of breath is accompanied by chest pain, especially if the pain radiates to your arm, neck, or jaw, this could be a sign of a heart attack. This symptom combination should never be ignored, and immediate medical attention is necessary.
Worsening of Chronic Conditions: For individuals with chronic conditions such as asthma or COPD, a sudden worsening of symptoms—like increased breathlessness, wheezing, or a significant drop in oxygen levels—could indicate a flare-up or infection. These changes may require adjustments in treatment or additional medications to prevent further complications.
- Sudden, severe breathlessness: Possible heart attack, pulmonary embolism, or pneumothorax
- Breathlessness with chest pain: Potential heart attack, seek emergency care
- Worsening chronic conditions: Could signal flare-up or infection, consult a healthcare provider
Breathing Exercises for Relief
Breathing exercises are a simple yet effective way to manage shortness of breath at home. They can help calm the mind, improve oxygen exchange, and strengthen the respiratory muscles. Regular practice of these exercises can lead to significant improvements in breathing efficiency and reduce the sensation of breathlessness during daily activities.

Pursed-Lip Breathing: This exercise helps slow down your breathing rate and keeps your airways open longer, allowing more air to enter and exit your lungs. To perform pursed-lip breathing, inhale slowly through your nose for a count of two, then purse your lips as if you’re about to blow out a candle and exhale slowly through your lips for a count of four. Repeat this exercise for several minutes until you feel more relaxed and your breathing steadies.
Diaphragmatic Breathing: Also known as belly breathing, diaphragmatic breathing engages the diaphragm—a major muscle involved in breathing—rather than relying on the accessory muscles in the neck and shoulders. To practice this exercise, sit or lie down in a comfortable position. Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. Breathe in deeply through your nose, allowing your abdomen to expand while keeping your chest still. Exhale slowly through pursed lips, feeling your abdomen fall. Repeat this process for several minutes, focusing on deep, even breaths.
Deep Breathing: Deep breathing exercises can help increase lung capacity and reduce anxiety, which often accompanies shortness of breath. Find a comfortable, quiet place to sit or lie down. Take a slow, deep breath in through your nose, filling your lungs completely. Hold your breath for a moment, then slowly exhale through your mouth. Repeat this exercise several times, aiming to deepen each breath progressively.
- Pursed-lip breathing: Inhale through nose, exhale through pursed lips
- Diaphragmatic breathing: Focus on belly movement, not chest
- Deep breathing: Deep inhalation and slow exhalation to expand lung capacity
Adjusting Your Environment
Creating a supportive environment is a vital aspect of managing shortness of breath at home. Simple changes in your surroundings can reduce the triggers of breathlessness and make it easier to breathe. By optimizing air quality, managing allergens, and ensuring adequate ventilation, you can create a more comfortable space that supports your respiratory health.

Improve Ventilation: Proper ventilation helps to circulate fresh air throughout your home, reducing the concentration of indoor pollutants that can aggravate shortness of breath. Open windows regularly, use exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms, and consider installing an air exchange system to improve indoor air quality.
Control Allergens: Allergens such as dust mites, mold, pet dander, and pollen can trigger respiratory issues. To minimize exposure, keep your home clean and dust-free by vacuuming frequently with a HEPA filter vacuum, washing bedding regularly in hot water, and using dust mite covers on pillows and mattresses. Additionally, maintaining low humidity levels can help prevent mold growth.
Use Air Purifiers: Air purifiers equipped with HEPA filters can remove airborne particles, including allergens and pollutants, from your home environment. Place air purifiers in commonly used areas, such as bedrooms and living rooms, to continuously filter the air and reduce potential triggers of breathlessness.
- Ventilation: Open windows, use exhaust fans, consider air exchange systems
- Allergen control: Regular cleaning, dust mite covers, low humidity
- Air purifiers: Use HEPA filters to remove airborne particles
Using Humidity Control
Maintaining the right level of humidity in your home is crucial for respiratory comfort, especially if you suffer from shortness of breath. Both excessively dry and overly humid environments can irritate your airways and worsen breathing difficulties. By managing humidity levels, you can create a more favorable atmosphere that supports easier breathing.

Managing Dry Air: Dry air can irritate the mucous membranes in your respiratory tract, leading to coughing, dryness, and increased shortness of breath. Using a humidifier can add moisture to the air, helping to keep your airways hydrated and more comfortable. Aim to maintain indoor humidity levels between 30% and 50%, as excessively high humidity can promote mold growth and dust mites, which are common allergens.
Controlling Excess Humidity: High humidity can make breathing feel more labored and can contribute to the growth of mold and mildew, which are known respiratory irritants. To reduce humidity, use a dehumidifier, especially in damp areas like basements or bathrooms. Air conditioning can also help control indoor humidity levels by removing moisture from the air. Regularly empty and clean dehumidifiers to prevent mold buildup.
Monitoring Humidity Levels: Using a hygrometer, a device that measures the level of humidity in the air, can help you keep track of the indoor humidity in your home. By keeping humidity within the recommended range, you can reduce the strain on your respiratory system and make breathing easier. Adjust the settings on your humidifiers and dehumidifiers as needed to maintain the optimal balance.
- Dry air: Use a humidifier to add moisture, target 30%-50% humidity
- Excess humidity: Use dehumidifiers or air conditioning to reduce moisture
- Monitoring: Use a hygrometer to track and adjust humidity levels
Diet and Nutrition Tips
Diet and nutrition play a significant role in managing shortness of breath, particularly if your condition is influenced by chronic respiratory issues, obesity, or general health concerns. A well-balanced diet can improve your overall health, boost your immune system, and support better lung function. Making mindful food choices can help reduce inflammation, maintain a healthy weight, and provide the necessary nutrients to support respiratory health.

Focus on Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Inflammation in the airways can exacerbate shortness of breath. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats like olive oil and omega-3 fatty acids from fish, can help reduce inflammation in the body. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, nuts, and green leafy vegetables, can also support lung health by protecting cells from oxidative stress.
Avoid Foods That Cause Bloating: Bloating can put additional pressure on the diaphragm and lungs, making it more difficult to breathe. Foods that can cause bloating include carbonated drinks, beans, cabbage, and fried foods. Limiting these foods, especially before physical activity or bedtime, can help reduce the feeling of breathlessness associated with bloating.
Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for maintaining healthy mucous membranes in the airways. Drinking adequate water helps keep the mucous lining of the respiratory tract thin and easier to clear, which can alleviate some of the discomfort associated with shortness of breath. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day, and consider herbal teas or clear broths as additional fluid sources.
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats
- Avoid bloating foods: Carbonated drinks, beans, cabbage, fried foods
- Hydration: Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is critical for individuals experiencing shortness of breath, as excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, can restrict the diaphragm and impair lung function. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly improve your breathing and overall well-being. Even modest weight loss can lead to noticeable improvements in respiratory function.
Impact of Excess Weight on Breathing: Extra weight, especially around the midsection, increases the workload on your respiratory system. This added pressure can make breathing more laborious, particularly during physical activities or when lying down. Reducing body weight can alleviate this pressure, allowing your diaphragm and lungs to function more efficiently.
Incorporating Physical Activity: Regular physical activity is not only beneficial for weight management but also strengthens the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Start with low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling, which are easier on the joints and can be gradually intensified as your endurance improves. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by health guidelines.
Balanced Diet for Weight Management: A balanced diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, provides essential nutrients without excessive calories. Avoid high-calorie, low-nutrient foods such as sugary snacks, processed foods, and fried items. Focus on portion control and mindful eating to prevent overeating and support gradual, sustainable weight loss.
- Excess weight impact: Increases pressure on diaphragm, impairs lung function
- Physical activity: Engage in low-impact exercises, aim for 150 minutes per week
- Balanced diet: Prioritize whole foods, control portions, avoid high-calorie snacks
Stress Management Techniques
Stress and anxiety can significantly contribute to episodes of shortness of breath. When you are stressed or anxious, your body may react with rapid, shallow breathing, which can lead to a feeling of breathlessness. Implementing stress management techniques can help calm your mind and body, making it easier to maintain steady, controlled breathing even in challenging situations.

Practice Mindful Breathing: Mindful breathing is a simple yet effective technique to manage stress and regulate breathing patterns. Find a quiet place to sit comfortably. Close your eyes and focus on your breath, noticing each inhalation and exhalation without trying to change it. Gradually, deepen your breath by inhaling slowly through your nose, holding it briefly, and exhaling gently through your mouth. This exercise helps slow your heart rate, reduce stress, and improve oxygen flow.
Incorporate Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, and body scanning can help reduce physical tension and promote relaxation. For example, progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups in your body, starting from your toes and working up to your head. This method can help you become more aware of physical tension and learn to release it, making breathing easier.
Engage in Activities That Promote Relaxation: Regular engagement in activities that you enjoy and find relaxing can help keep stress levels in check. This might include hobbies such as reading, gardening, listening to music, or practicing yoga. Physical activities, especially those that are rhythmic and repetitive like walking or swimming, can also be particularly calming. These activities not only distract from stress but also enhance overall well-being and respiratory function.
- Mindful breathing: Focus on slow, deep breaths to calm the mind
- Relaxation techniques: Progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery
- Relaxing activities: Hobbies, yoga, rhythmic exercises
Identifying Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers is a crucial step in preventing shortness of breath episodes. By understanding what specifically causes or worsens your breathlessness, you can take proactive measures to minimize exposure and manage your symptoms more effectively. Triggers can vary greatly among individuals, so it’s important to personalize your approach based on your unique experiences and health conditions.

Common Environmental Triggers: Environmental factors such as air pollution, extreme weather conditions, smoke, and strong odors can aggravate shortness of breath. Allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold are also common triggers for many people. Keeping your living environment clean, using air filters, and avoiding outdoor activities during high pollen seasons or when air quality is poor can help reduce your exposure to these triggers.
Physical Exertion and Overexertion: Physical activity is beneficial for lung health, but overexertion can lead to shortness of breath, especially in individuals with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions. Identifying your physical limits and gradually building up your activity level can help you stay active without overwhelming your respiratory system. Pacing yourself during exercise, taking frequent breaks, and engaging in low-impact activities can help you maintain an active lifestyle while managing breathlessness.
Emotional and Psychological Triggers: Stress, anxiety, and panic can trigger or worsen shortness of breath. Recognizing the connection between your emotional state and breathing can help you implement coping strategies when needed. Practicing relaxation techniques, seeking support from friends, family, or mental health professionals, and managing stress through hobbies or mindfulness practices can reduce the impact of emotional triggers on your breathing.
- Environmental triggers: Air pollution, allergens, extreme weather, strong odors
- Physical exertion: Avoid overexertion, pace your activities, choose low-impact exercises
- Emotional triggers: Manage stress and anxiety through relaxation techniques and support
Regular Exercise and Its Benefits
Regular exercise is an essential component of managing shortness of breath, as it helps improve lung function, increase stamina, and enhance overall cardiovascular health. While it may seem counterintuitive to engage in physical activity when experiencing breathlessness, carefully tailored exercise routines can help reduce the severity of symptoms over time. Consistent exercise can strengthen the muscles used in breathing, making your respiratory system more efficient.

Benefits of Cardiovascular Exercise: Cardiovascular exercises, such as walking, swimming, and cycling, improve the efficiency of your heart and lungs. These activities increase your body’s ability to use oxygen, which can help alleviate shortness of breath during physical exertion. Start with low-intensity exercises and gradually increase the duration and intensity as your fitness improves. Consistency is key, so aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Incorporating Strength Training: Strength training exercises can also be beneficial, as they build muscle endurance and support overall physical health. By strengthening the muscles that assist in breathing, such as the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, you can improve your body’s ability to handle everyday activities without excessive breathlessness. Include exercises like resistance band workouts, light weightlifting, or bodyweight exercises in your routine at least two times per week.
Stretching and Flexibility Exercises: Stretching and flexibility exercises, such as yoga or tai chi, can improve posture and open up the chest, allowing for better lung expansion and easier breathing. These activities also incorporate deep breathing techniques, which can help relax the body and reduce the sensation of breathlessness. Gentle stretching before and after exercise sessions can also help prevent muscle strain and promote recovery.
- Cardiovascular exercise: Walking, swimming, cycling for improved oxygen use
- Strength training: Builds muscle endurance, supports breathing muscles
- Flexibility exercises: Yoga, tai chi for improved posture and deep breathing
Avoiding Pollutants and Allergens
Exposure to pollutants and allergens is a common trigger for shortness of breath, particularly for individuals with respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD. By minimizing exposure to these irritants, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of breathlessness episodes. Implementing strategies to control the air quality in your environment is essential for maintaining optimal respiratory health.
Minimize Exposure to Air Pollution: Air pollution, including vehicle emissions, industrial fumes, and indoor pollutants like cigarette smoke, can irritate the airways and exacerbate breathing difficulties. Avoid outdoor activities on days when air quality is poor, as indicated by air quality indexes. At home, consider using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters in your HVAC system or standalone air purifiers to reduce indoor pollution levels.
Control Indoor Allergens: Common indoor allergens, such as dust mites, mold spores, pet dander, and pollen, can aggravate shortness of breath. To control these allergens, keep your home clean by regularly vacuuming with a HEPA filter vacuum, washing bedding in hot water weekly, and reducing clutter where dust can accumulate. For mold control, ensure that damp areas, like bathrooms and basements, are well-ventilated and use dehumidifiers to keep humidity levels low.
Avoid Smoking and Secondhand Smoke: Smoking is one of the most significant contributors to respiratory problems and shortness of breath. If you smoke, seeking resources and support to quit can dramatically improve your lung health and breathing. Additionally, avoid exposure to secondhand smoke, which can be equally harmful. Implementing a smoke-free policy in your home and vehicle is an effective way to reduce exposure to tobacco-related irritants.
- Air pollution: Avoid outdoor activities on poor air quality days, use HEPA filters
- Indoor allergens: Regular cleaning, wash bedding, control humidity
- Avoid smoking: Quit smoking, avoid secondhand smoke exposure
FAQ
1. What are some immediate steps I can take when I experience shortness of breath at home?
If you experience shortness of breath, try to remain calm and sit in an upright position to help open your airways. Practice pursed-lip breathing to slow down your breathing rate and allow more air into your lungs. Make sure your environment is well-ventilated and free of irritants like smoke or strong odors.
2. Can diet affect my breathing?
Yes, diet can have a significant impact on breathing. Consuming a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce airway inflammation and improve respiratory health. Avoiding foods that cause bloating or acid reflux can also prevent additional pressure on the diaphragm, making it easier to breathe.
3. How can I prevent shortness of breath at night?
To prevent shortness of breath at night, ensure your sleeping environment is clean, free of allergens, and well-ventilated. Elevating your head with pillows can help keep airways open. Avoid heavy meals, alcohol, and smoking before bedtime, as these can worsen breathing issues while sleeping.
4. When should I seek medical attention for shortness of breath?
Seek medical attention if your shortness of breath is sudden, severe, or accompanied by chest pain, dizziness, or a high fever. These symptoms could indicate a serious medical condition that requires immediate intervention. If you have a chronic condition and notice a significant worsening of symptoms, consult your healthcare provider.
5. Are there long-term strategies to manage chronic shortness of breath?
Long-term strategies include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding known triggers, managing stress, and following a healthy diet. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider and adhering to prescribed medications or therapies are also important for managing chronic shortness of breath effectively.

