What is an EKG and Why is it Important?
Understanding Your EKG Results. An Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a medical test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It’s a crucial tool for diagnosing various heart conditions, from arrhythmias to heart attacks. Understanding your EKG results can provide insight into your heart’s health, guiding your healthcare provider in making important decisions about your treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
The EKG test is non-invasive, quick, and painless. Electrodes are placed on the skin to detect and record the heart’s electrical signals, which are then represented as waves on a graph. These waves correspond to different phases of the heart’s activity, such as the contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles. Interpreting these signals accurately is essential for diagnosing heart issues and monitoring ongoing heart health.
- It helps detect abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias).
- It can identify poor blood flow to the heart muscle (ischemia).
- It detects changes in the heart muscle, such as thickening or damage.
- It provides clues about electrolyte imbalances that can affect heart function.
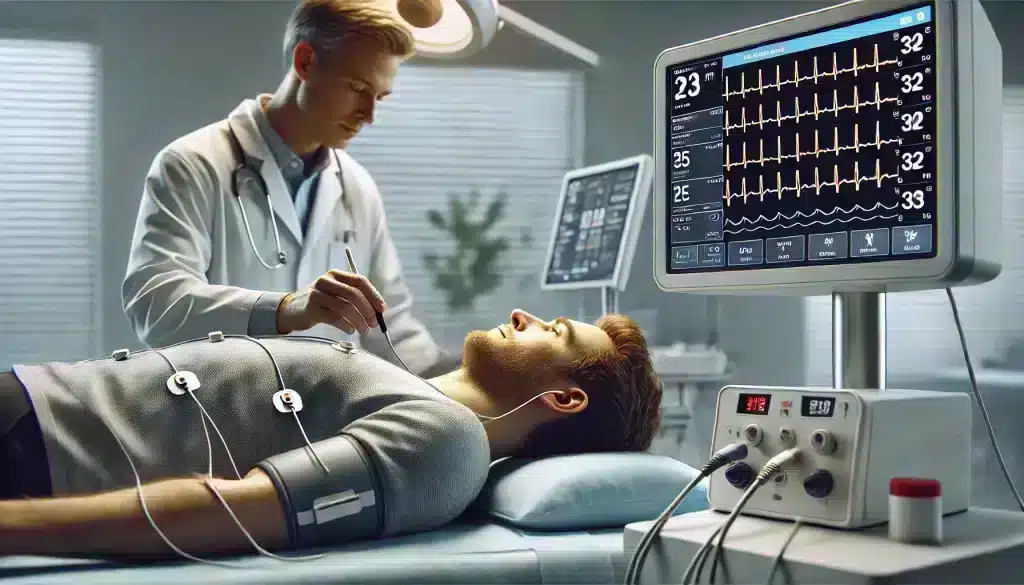
How to Prepare for an EKG Test
Preparing for an EKG test is simple, but taking a few steps in advance can help ensure accurate results. Before the test, inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking, as some substances can affect the heart’s electrical activity. Here are some guidelines to help you prepare for an EKG:
- Avoid caffeine and heavy meals: Consuming caffeine or eating a large meal right before the test can alter your heart rate, potentially affecting the EKG results.
- Wear comfortable clothing: It’s best to wear a loose-fitting shirt that can be easily removed, as the test requires electrodes to be placed on your chest, arms, and legs.
- Stay relaxed: Anxiety or stress can cause changes in your heart rhythm. Try to relax and breathe normally during the test for the most accurate readings.
- Avoid using lotions or creams: These can interfere with the electrode placement and the quality of the recordings, so it’s best to skip them on the day of the test.
By following these simple steps, you can help ensure that your EKG provides the clearest and most accurate picture of your heart’s electrical activity. Always follow any specific instructions given by your healthcare provider.

Key Components of an EKG Report
Understanding your EKG report starts with recognizing its key components. An EKG graph displays several waveforms, intervals, and segments that reflect the different phases of your heart’s electrical cycle. Each part of this graph provides specific information about how your heart is functioning, and a thorough interpretation can reveal important details about your heart health.
Heart Rate
The heart rate is one of the first things analyzed in an EKG. It is usually measured in beats per minute (BPM). A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 BPM. An EKG can quickly identify whether your heart rate is within this normal range or if there are any abnormalities such as bradycardia (slower than normal heart rate) or tachycardia (faster than normal heart rate). Deviations from the normal range can indicate underlying conditions like thyroid disorders, infections, or cardiac issues that require further evaluation and management.
Heart Rhythm
The rhythm of your heart is another critical aspect assessed by the EKG. The heart should beat in a consistent and regular pattern, known as a sinus rhythm, which originates from the heart’s natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial node. However, irregular rhythms, known as arrhythmias, can occur and are often detected by an EKG. Some arrhythmias are benign, while others, like atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, may be serious and require immediate medical intervention. Identifying the type of rhythm disturbance is crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment, which can range from medication adjustments to more invasive procedures like ablation or the implantation of a pacemaker.
Electrical Activity of the Heart
The EKG provides a detailed view of the heart’s electrical activity, including how electrical impulses travel through the heart muscle. This includes the P wave, which represents atrial contraction; the QRS complex, which reflects ventricular contraction; and the T wave, which indicates ventricular relaxation. Each of these components is analyzed for abnormalities in shape, size, and duration, as these can point to specific cardiac conditions. For example, prolonged QRS duration might suggest bundle branch block or other conduction issues, while abnormal T wave patterns could indicate electrolyte imbalances, ischemia, or even heart attack.
By breaking down these components, healthcare providers can diagnose a variety of heart conditions, assess the effectiveness of ongoing treatments, and monitor the overall health of your heart. A thorough understanding of these elements allows patients to have informed discussions with their healthcare providers about their heart health and potential next steps in their care.
Common EKG Patterns and What They Indicate
An EKG can reveal a wide array of heart conditions based on the patterns it captures. These patterns are crucial for diagnosing normal and abnormal heart functions. Recognizing these patterns helps healthcare providers determine whether the heart is functioning correctly or if there are underlying issues that require further investigation or immediate intervention.
Normal EKG
A normal EKG shows a consistent and predictable pattern that reflects the proper functioning of the heart’s electrical system. The P wave appears smooth and uniform, followed by the QRS complex, which is narrow and well-defined, indicating efficient contraction of the ventricles.
The T wave, representing ventricular relaxation, should also be smooth and upright. This pattern suggests that the heart is beating in a regular sinus rhythm without any signs of arrhythmias or other abnormalities. A normal EKG result provides reassurance that the heart’s electrical activity is within the expected range, reflecting good overall heart health. However, even a normal EKG does not rule out all heart conditions, so it is essential for patients to discuss any ongoing symptoms with their healthcare provider.
Abnormal EKG: What to Watch For
Abnormal EKG results can manifest in various ways, depending on the specific issue with the heart’s electrical activity. Common abnormalities include irregular rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation, which appears as an erratic baseline with absent P waves and irregularly spaced QRS complexes. Another common abnormal pattern is ST-segment elevation or depression, which can indicate acute coronary syndrome, such as a heart attack. ST-segment changes are critical markers and often prompt immediate medical action to restore blood flow to the heart.
Other abnormal patterns may include prolonged QT intervals, which can be a sign of electrolyte imbalances or genetic conditions that increase the risk of life-threatening arrhythmias. Additionally, findings like inverted T waves or abnormal Q waves might suggest past heart damage, such as from a previous heart attack or ongoing ischemia. Identifying these patterns allows healthcare providers to diagnose conditions early, potentially preventing severe complications through timely medical intervention.
Overall, understanding these common EKG patterns empowers patients to be proactive about their heart health. Recognizing the significance of each wave and interval on an EKG helps in identifying both benign and severe cardiac conditions, aiding in swift and effective treatment decisions.
What Factors Can Affect EKG Results?
Several factors can influence the accuracy and interpretation of EKG results. These factors range from technical issues during the test to physiological conditions that can alter the heart’s electrical activity. Understanding these variables is crucial for ensuring that the EKG results reflect an accurate representation of the heart’s health, and it helps in distinguishing between true abnormalities and artifacts or external influences.
Medications: Many medications can affect the heart’s electrical signals. For instance, drugs like beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and certain antidepressants can alter heart rate and rhythm, potentially impacting the EKG readings. It is essential for patients to inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as these can sometimes cause unexpected changes in EKG results.
Electrolyte Imbalances: Electrolytes such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium play a significant role in the heart’s electrical activity. Imbalances in these minerals can cause changes in the EKG, such as alterations in the T wave or QT interval. For example, hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) can lead to tall, peaked T waves, while hypokalemia (low potassium levels) might cause flattened or inverted T waves. Correcting these imbalances often resolves the related EKG abnormalities, highlighting the importance of maintaining balanced electrolyte levels for heart health.
Body Position and Movement: How a patient is positioned during the EKG test can also impact the results. Ideally, patients should be lying still on their back, as movement or changes in position can cause shifts in the baseline or introduce noise into the recordings, leading to misinterpretations. Muscle tremors, shivering, or even talking during the test can create artifacts that mimic arrhythmias or other heart conditions, emphasizing the need for patients to remain calm and still throughout the procedure.
Technical Issues: Poor electrode contact or incorrect placement can significantly affect the quality of the EKG readings. Ensuring that the skin is clean and dry and that electrodes are firmly attached can help reduce the risk of poor signal quality. In some cases, incorrect calibration of the EKG machine itself can lead to inaccurate results, making routine equipment checks and maintenance essential for reliable readings.
Recognizing these factors and taking steps to mitigate them can greatly enhance the reliability of EKG results. It also underscores the importance of healthcare providers conducting a thorough review of the patient’s overall health and any potential external influences that could impact the EKG interpretation.
Understanding Your Doctor’s Interpretation
After your EKG is completed, your doctor will review the results to provide an interpretation of what they mean for your heart health. This interpretation is based on a careful analysis of the waveforms, intervals, and segments seen on the EKG graph. Your doctor will compare these findings to standard values to determine if everything falls within normal ranges or if there are any signs of heart problems.
One of the key things your doctor will look for is the overall rhythm of your heart. They will assess whether it is a normal sinus rhythm, which indicates a healthy heartbeat originating from the heart’s natural pacemaker, or if there are any irregular rhythms that need attention. Your doctor will also evaluate the heart rate and look for signs of arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, which may require further testing or treatment.
In addition to rhythm and rate, your doctor will assess the size and shape of the various waves on the EKG. Abnormalities in these waves can provide clues about different cardiac conditions. For example, enlarged P waves might suggest atrial enlargement, while abnormalities in the QRS complex could indicate issues such as ventricular hypertrophy or bundle branch block. The doctor will also scrutinize the ST segment and T wave for signs of ischemia or previous heart attacks.
Your doctor’s interpretation is crucial in guiding the next steps for your care. If your EKG is normal, it may simply serve as a baseline for future comparisons. However, if abnormalities are found, your doctor may recommend additional tests, such as an echocardiogram or a stress test, to further investigate the findings. Understanding your doctor’s interpretation allows you to be more engaged in your care and helps you make informed decisions about your heart health.
FAQs: Common Questions About EKG Results
What do abnormal EKG results mean?
Abnormal EKG results can indicate a variety of heart conditions, ranging from minor issues to more serious problems. Common abnormalities include irregular heart rhythms, signs of past or ongoing heart attacks, and evidence of enlarged heart chambers. Abnormal EKG findings can also suggest electrolyte imbalances, conduction abnormalities like bundle branch blocks, or even the effects of medications that alter the heart’s electrical activity. It is important to discuss any abnormal results with your doctor, who can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate next steps, whether it’s lifestyle changes, medications, or further diagnostic tests.
Can stress or anxiety affect EKG results?
Yes, stress and anxiety can impact EKG results by affecting your heart rate and rhythm. When you are stressed or anxious, your body releases adrenaline, which can cause your heart to beat faster and sometimes irregularly. This response can result in an elevated heart rate or premature heartbeats, which might be reflected on the EKG as sinus tachycardia or other rhythm irregularities. Although these findings are often benign, it is crucial to inform your healthcare provider about your emotional state during the test, as this can help them interpret the results more accurately and differentiate between stress-related changes and those that may indicate a true heart condition.
How often should I get an EKG?
The frequency of EKG testing depends on your individual health status and risk factors. For healthy individuals with no symptoms or risk factors for heart disease, routine EKG testing is not typically necessary. However, if you have symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, or dizziness, or if you have risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease, your doctor may recommend more frequent EKGs.
For patients with known heart conditions, regular EKGs might be part of ongoing monitoring to assess the effectiveness of treatments or to detect changes in heart function over time. Always follow your doctor’s advice regarding how often you should have an EKG based on your specific health needs.